Obstetrics Treatments
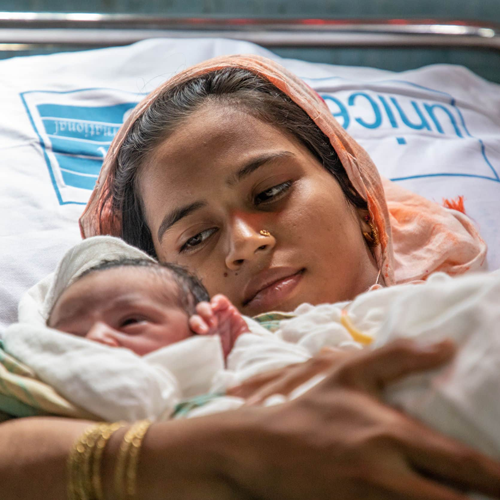

Management prevention and Antenatal care
Management prevention refers to strategies and actions taken to prevent or mitigate potential issues within an organization. It involves proactive measures to identify and address risks, challenges, and obstacles before they escalate.
Antenatal CareAntenatal care is healthcare provided to pregnant women before childbirth. It is a crucial aspect of maternal health, aiming to monitor and promote the well-being of both the mother and the developing.
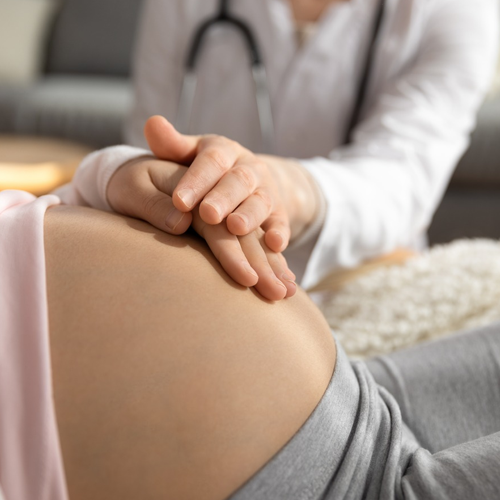

Intrapartum Care & Postpartum Care
Intrapartum care refers to the care and support provided to a woman during the process of childbirth, from the onset of labor to the delivery of the baby and the immediate postpartum period.
Postpartum CarePostpartum care involves the care and support provided to a woman and her baby in the period following childbirth, usually extending for several weeks to address recovery, breastfeeding, and adjustment to parenthood.
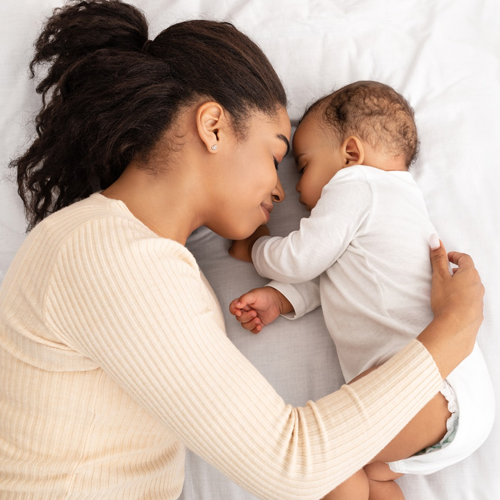

Maternal & Child Health
Maternal and child health (MCH) is a critical component of public health that focuses on the well-being of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, as well as the health and development of infants and children. The importance of MCH lies not only in promoting healthy outcomes for mothers and their offspring but also in contributing to the overall health and prosperity of communities One of the primary goals of MCH is to ensure safe and healthy pregnancies.
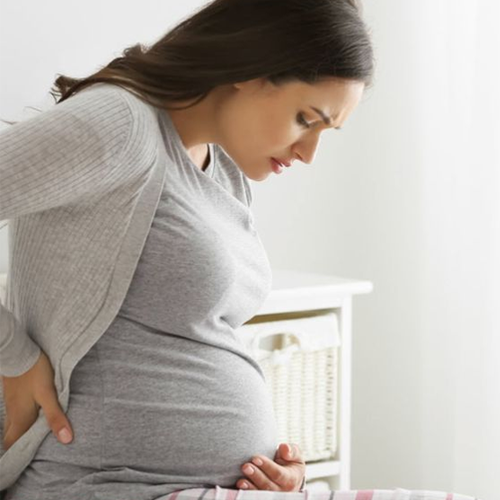

High Risk Pregnancy
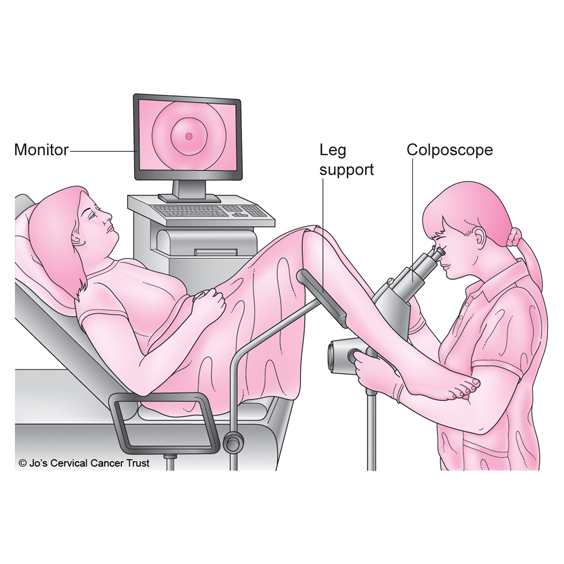
Management of a high-risk pregnancy involves vigilant monitoring and specialized care. This often includes more frequent prenatal visits to closely track the progression of the pregnancy and assess potential issues. Specialized tests and screenings may be employed to detect and address complications early on. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary adjustments and appropriate exercise, are often recommended to optimize maternal and fetal health. Medications or medical interventions .